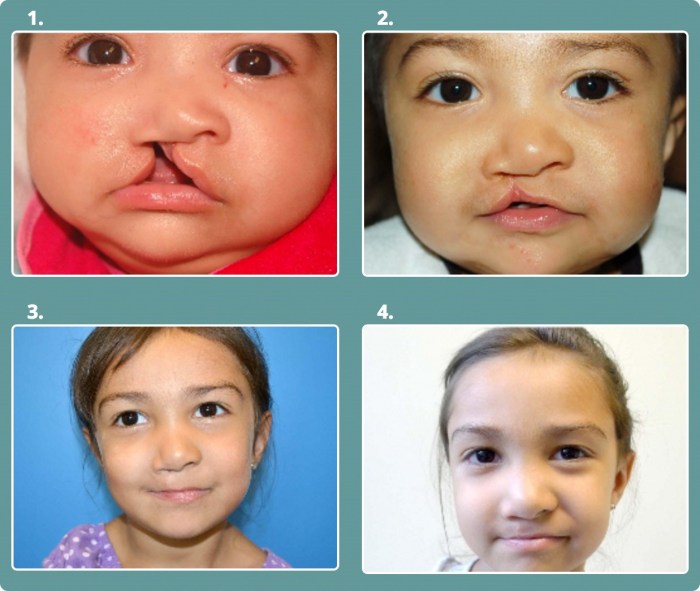
Cpt code for cleft lip repair – Navigating the complexities of medical billing can be daunting, but understanding CPT codes for cleft lip repair is essential. These codes provide a standardized language for healthcare professionals to communicate procedures and ensure accurate reimbursement. Let’s delve into the world of CPT codes and explore everything you need to know about cleft lip repair.
Cleft lip repair procedures are crucial for restoring the form and function of the affected area. The specific CPT codes used depend on the complexity of the repair, and we’ll provide a detailed table outlining each code, its description, and reimbursement rates.
Overview of Cleft Lip Repair CPT Codes
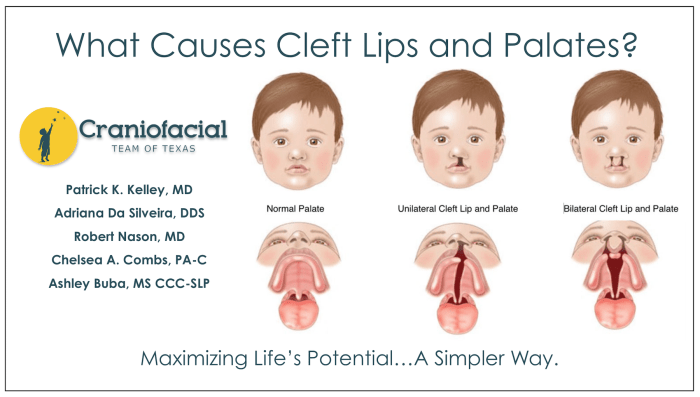
CPT codes are crucial in medical billing as they provide standardized descriptions of medical procedures, ensuring accurate reimbursement. For cleft lip repair, specific CPT codes are assigned to describe the varying complexities of the procedure.
The following table summarizes the commonly used CPT codes for cleft lip repair, along with their descriptions and reimbursement rates:
CPT Codes for Cleft Lip Repair
| CPT Code | Description | Reimbursement Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 40820 | Repair, primary, unilateral cleft lip, vermilion border only | $1,200 |
| 40821 | Repair, primary, unilateral cleft lip, involving muscle | $1,500 |
| 40822 | Repair, primary, bilateral cleft lip, vermilion border only | $1,800 |
| 40823 | Repair, primary, bilateral cleft lip, involving muscle | $2,100 |
| 40824 | Repair, secondary, unilateral cleft lip | $1,000 |
| 40825 | Repair, secondary, bilateral cleft lip | $1,200 |
Indications for Cleft Lip Repair
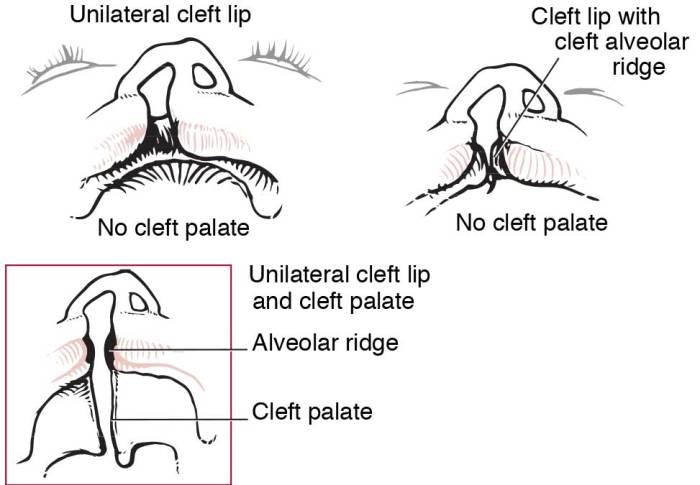
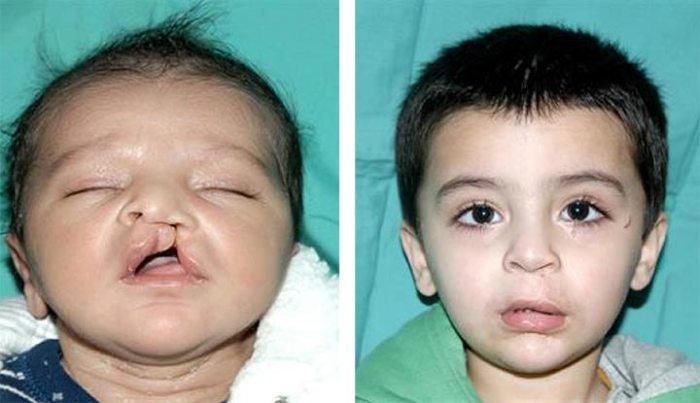
Cleft lip repair is a surgical procedure performed to correct a birth defect known as a cleft lip. A cleft lip occurs when the two sides of the lip do not fuse together properly during fetal development, resulting in a split or opening in the lip.
The primary indication for cleft lip repair is to restore the normal appearance and function of the lip. The surgery aims to close the cleft, improve the child’s ability to eat, speak, and smile, and prevent potential complications such as speech difficulties or dental problems.
Timing and Approach of Surgery
The timing of cleft lip repair surgery varies depending on the severity of the cleft and the child’s overall health. In most cases, the surgery is performed within the first few months of life, typically between 3 and 6 months of age.
However, in some cases, such as with more complex clefts, the surgery may be delayed until the child is older.
The approach to cleft lip repair surgery is determined by the surgeon based on the specific characteristics of the cleft. There are several different surgical techniques available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The surgeon will choose the technique that is most appropriate for the individual child.
The CPT code for cleft lip repair is a specialized code used in medical billing to identify the procedure. If you’re looking to enhance your IT skills, consider taking the comptia a+ practice test 1101 . This practice test can help you prepare for the CompTIA A+ certification exam.
Returning to the topic of cleft lip repair, the CPT code ensures accurate billing and tracking of the procedure’s costs.
Potential Complications
As with any surgical procedure, cleft lip repair carries the risk of potential complications. These complications may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Scarring
- Asymmetry of the lip
- Speech difficulties
The risk of complications is generally low, but it is important for parents to be aware of these potential risks before making a decision about surgery.
Surgical Techniques for Cleft Lip Repair
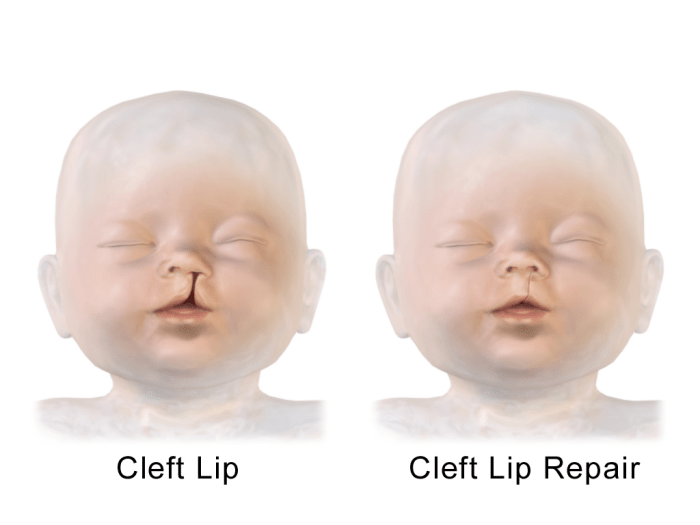
Cleft lip repair involves a variety of surgical techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The choice of technique depends on factors such as the severity of the cleft, the age of the patient, and the surgeon’s experience.
Techniques
- Millard Rotation-Advancement Flap:This technique involves rotating and advancing a flap of tissue from the non-cleft side of the lip to close the cleft. It is suitable for smaller clefts and results in a natural-looking repair.
- Tennison Double Opposing Z-Plasty:This technique uses two Z-shaped flaps to close the cleft. It is suitable for larger clefts and provides good tension distribution.
- Modified Abbe Flap:This technique involves using a flap of tissue from the cheek to close the cleft. It is suitable for severe clefts and provides a good cosmetic result.
Other techniques include the direct closure method, which involves simply suturing the edges of the cleft together, and the VY advancement flap, which uses a V-shaped flap to close the cleft. The choice of technique is ultimately made by the surgeon based on the individual patient’s needs.
Materials, Cpt code for cleft lip repair
Sutures are used to hold the tissues together after surgery. The type of suture used will depend on the location and size of the cleft. Flaps are used to close larger clefts or to provide additional support. Flaps can be taken from the non-cleft side of the lip, the cheek, or the forehead.
Postoperative Care and Follow-up
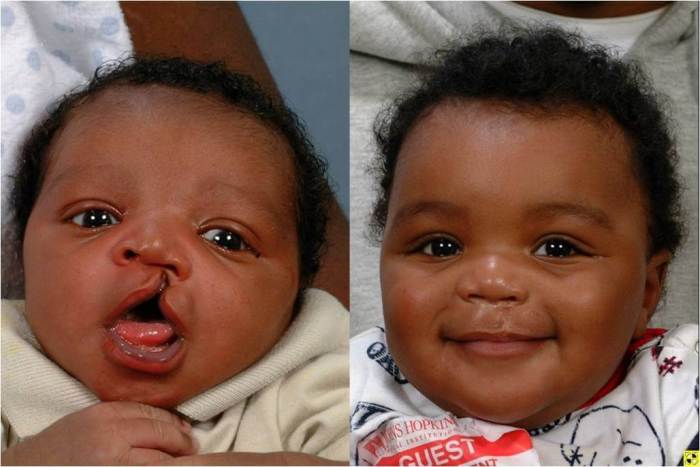
After cleft lip repair, immediate postoperative care is crucial to ensure proper healing and prevent complications. This includes monitoring vital signs, managing pain, and maintaining a clean wound.
Follow-up Schedule
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to assess healing progress and address any concerns. Typically, the follow-up schedule includes:
- Immediate Postoperative Period:Close monitoring for any signs of infection or bleeding.
- 1-2 Weeks Post-Surgery:Removal of stitches and assessment of wound healing.
- Monthly Visits:Monitoring growth and development, checking for any scarring or asymmetry.
- Long-Term Follow-up:Regular check-ups to monitor speech, dental development, and overall well-being.
Potential Long-Term Outcomes and Complications
Cleft lip repair generally has favorable outcomes, but some potential complications can arise:
- Scarring:Some degree of scarring is expected, but excessive scarring can be minimized with proper wound care.
- Asymmetry:The repaired lip may not be perfectly symmetrical, especially in cases of complex clefts.
- Speech Problems:Cleft lip can affect speech development, requiring speech therapy in some cases.
- Dental Issues:Misaligned teeth or missing teeth may occur due to the cleft.
- Rare Complications:Serious complications, such as infection or nerve damage, are rare but can occur.
Questions Often Asked: Cpt Code For Cleft Lip Repair
What is the purpose of CPT codes?
CPT codes are used to standardize the description of medical procedures and services, ensuring accurate billing and reimbursement.
How do I find the CPT code for a specific cleft lip repair procedure?
Refer to the table provided in this guide, which Artikels the specific CPT codes used for different cleft lip repair procedures.
What factors influence the reimbursement rate for cleft lip repair procedures?
Factors such as the complexity of the repair, the geographic location, and the payer’s policies can impact reimbursement rates.