Match the following barrett’s esophagus – Match the following: Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus is replaced by metaplasia of columnar epithelium. This condition is often associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and can lead to esophageal adenocarcinoma if left untreated.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the definition, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention, management, and potential complications of Barrett’s esophagus. By understanding this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Definition of Barrett’s Esophagus
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus is replaced by metaplasia of columnar epithelium with goblet cells. It is considered a premalignant condition, as it is associated with an increased risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma.
The characteristics of Barrett’s esophagus include:
- Presence of columnar epithelium with goblet cells in the distal esophagus
- Replacement of the normal squamous epithelium
- Increased risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma
The causes and risk factors of Barrett’s esophagus are not fully understood, but it is believed to be associated with chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Barrett’s Esophagus
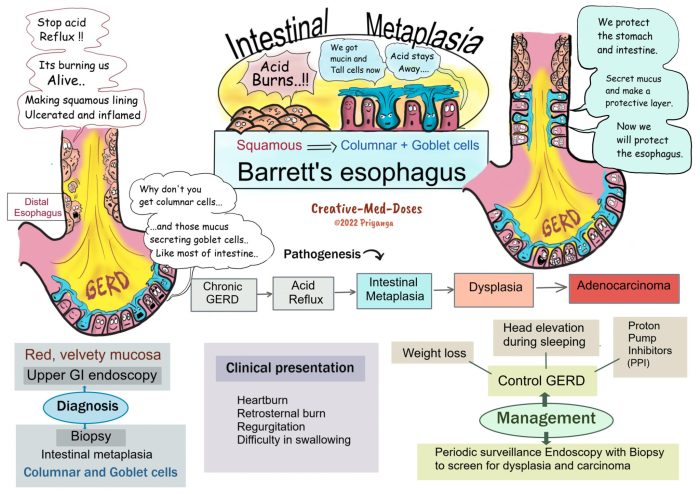
The most common symptom of Barrett’s esophagus is heartburn. Other symptoms may include:
- Regurgitation
- Dysphagia
- Chest pain
Barrett’s esophagus is diagnosed through endoscopy, a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end is inserted into the esophagus. During endoscopy, a biopsy may be taken to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Barrett’s Esophagus

The treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
- Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR)
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
- Cryotherapy
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s individual circumstances.
Prevention and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus: Match The Following Barrett’s Esophagus
There is no sure way to prevent Barrett’s esophagus, but there are some lifestyle modifications that may help to reduce the risk, including:
- Losing weight if overweight or obese
- Eating a healthy diet
- Avoiding smoking
- Limiting alcohol intake
Regular follow-up care is important for monitoring Barrett’s esophagus and detecting any complications early.
Complications of Barrett’s Esophagus
The most serious complication of Barrett’s esophagus is esophageal adenocarcinoma. Other complications may include:
- Stricture formation
- Ulceration
- Bleeding
The risk of developing complications is increased in patients with long-segment Barrett’s esophagus and high-grade dysplasia.
Questions Often Asked
What is Barrett’s esophagus?
Barrett’s esophagus is a condition in which the squamous epithelium of the distal esophagus is replaced by metaplasia of columnar epithelium.
What are the symptoms of Barrett’s esophagus?
The most common symptoms of Barrett’s esophagus include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
How is Barrett’s esophagus diagnosed?
Barrett’s esophagus is diagnosed through an endoscopy, a procedure in which a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to visualize the lining of the esophagus.
What are the treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus?
Treatment options for Barrett’s esophagus include lifestyle modifications, medications, endoscopic therapies, and surgery.
What are the complications of Barrett’s esophagus?
The most serious complication of Barrett’s esophagus is esophageal adenocarcinoma, a type of cancer that develops in the lining of the esophagus.