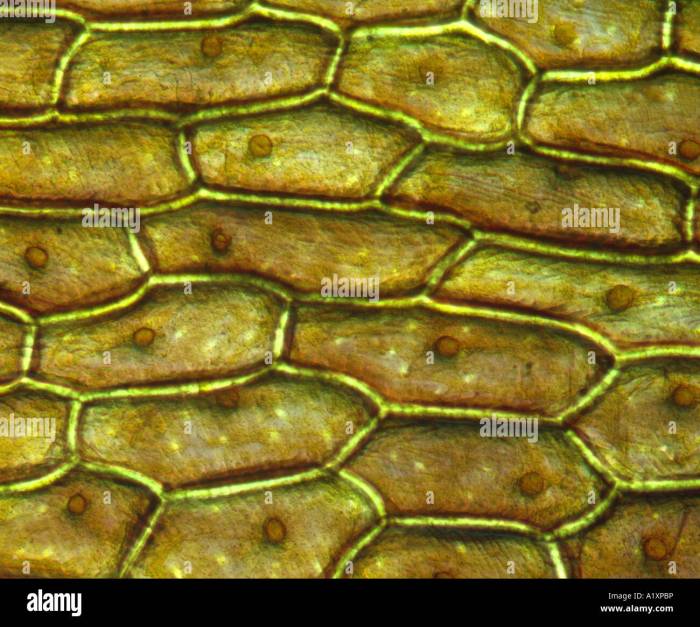
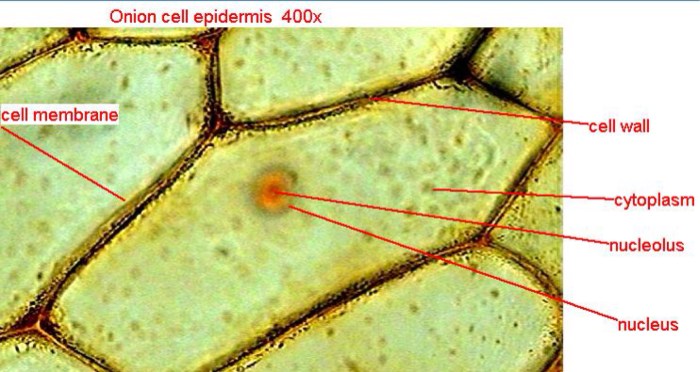
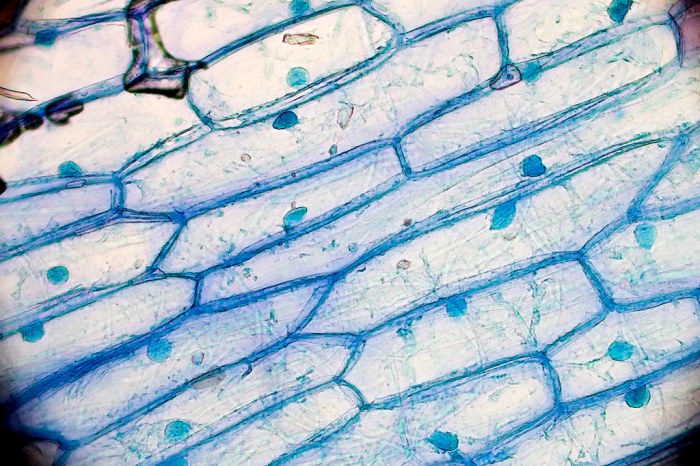
The onion cells i looked at have a nucleus – Embarking on an exploration of the onion cells I looked at, we unveil the captivating world of the nucleus, the control center of these plant cells. This microscopic marvel holds the blueprint for cellular life, orchestrating a symphony of functions that sustain and define the very essence of the cell.
Join us as we delve into the intricacies of this remarkable organelle, uncovering its structure, contents, and the pivotal role it plays in the life of an onion cell.
Within the confines of the onion cell, the nucleus reigns supreme, its presence discernible as a distinct, membrane-bound structure. Its shape and size vary, yet its significance remains constant. The nuclear envelope, a double membrane, safeguards the nucleus, regulating the passage of materials and ensuring the integrity of its contents.
The Nucleus of Onion Cells
The nucleus is a prominent organelle found in onion cells, as well as in all eukaryotic cells. It serves as the control center of the cell, housing the cell’s genetic material and directing various cellular activities.
Nucleus Structure
The nucleus is typically located in the center of the onion cell. It is a spherical or oval-shaped organelle, with a diameter ranging from 10 to 25 micrometers. The nucleus is enclosed by a double-membrane envelope called the nuclear envelope.
The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayers, with nuclear pores that allow for the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Nuclear Contents
Within the nucleus, several key components contribute to its functions. The nucleolus is a prominent structure within the nucleus that is responsible for ribosome production. Ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis, making the nucleolus crucial for cell growth and function.Chromatin
is another important component of the nucleus. It consists of DNA and proteins and forms a complex structure that contains the cell’s genetic information. The nuclear sap, or nucleoplasm, fills the remaining space within the nucleus. It contains enzymes, ions, and other molecules that support the functions of the nucleus.
Functions of the Nucleus, The onion cells i looked at have a nucleus
The nucleus plays a central role in controlling cellular activities. It houses the cell’s DNA, which contains the genetic instructions for all cellular functions. Through the process of transcription, the nucleus directs the production of messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized.The
nucleus also plays a crucial role in cell division. During mitosis, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the chromosomes condense to form visible structures. The chromosomes are then separated and distributed to the daughter cells, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material.
Comparing Onion Cells to Other Plant Cells
| Cell Type | Nucleus Size | Nuclear Features |
|---|---|---|
| Onion Cells | 10-25 micrometers | Spherical or oval shape, central location |
| Sunflower Cells | 20-30 micrometers | Irregular shape, multiple nucleoli |
| Corn Cells | 15-20 micrometers | Elongated shape, prominent nucleolus |
The nucleus of onion cells is similar to the nucleus of other plant cells in terms of its basic structure and functions. However, there can be variations in size, shape, and the presence of specific nuclear features among different plant species.
FAQ Guide: The Onion Cells I Looked At Have A Nucleus
What is the function of the nucleus in onion cells?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, directing cellular activities, including protein synthesis, cell division, and genetic inheritance.
How can I identify the nucleus in an onion cell?
The nucleus is typically the largest and most prominent organelle within the cell, often appearing as a distinct, membrane-bound structure.
What is the significance of the nuclear envelope?
The nuclear envelope regulates the movement of materials into and out of the nucleus, protecting its contents and maintaining the integrity of the cell.