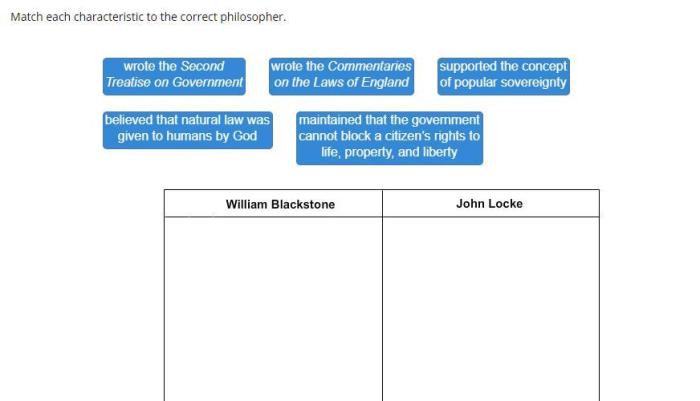
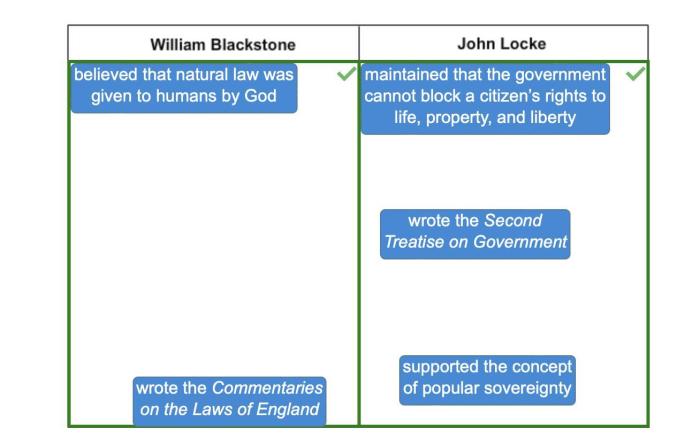
Match each philosophy to the correct philosopher. The study of philosophy delves into the profound ideas and influential thinkers that have shaped human understanding. By exploring the connections between philosophers and their philosophies, we embark on an intellectual journey that illuminates the evolution of thought and its impact on our world.
This comprehensive guide provides a structured approach to understanding the key tenets of various philosophies and the brilliant minds behind them. Through a meticulous examination of historical context, real-world applications, and potential debates, we unravel the intricate tapestry of philosophical thought.
Identify Philosophers
Philosophy has been a driving force in human civilization for centuries, shaping our understanding of the world and our place within it. Throughout history, countless philosophers have emerged, each with their own unique perspectives and contributions to the field.
Significant Philosophers, Match each philosophy to the correct philosopher.
- Socrates(469-399 BCE): Athenian philosopher known for his method of inquiry, known as the Socratic method, which emphasized critical thinking and self-examination.
- Plato(428-348 BCE): Student of Socrates, founded the Academy in Athens, and developed the theory of Forms, which posits that the physical world is merely a reflection of a higher, more perfect realm of existence.
- Aristotle(384-322 BCE): Student of Plato, founded the Lyceum in Athens, and developed a comprehensive system of philosophy that encompasses logic, metaphysics, ethics, and politics.
- René Descartes(1596-1650): French philosopher known for his famous dictum, “I think, therefore I am,” and his contributions to rationalism and the scientific method.
- Immanuel Kant(1724-1804): German philosopher who developed the theory of transcendental idealism, which posits that our knowledge of the world is shaped by the structure of our own minds.
- Karl Marx(1818-1883): German philosopher and economist who developed the theory of Marxism, which analyzes the relationship between economic systems and social structures.
- Friedrich Nietzsche(1844-1900): German philosopher known for his critique of traditional morality and his concept of the “Übermensch” (superman).
- Bertrand Russell(1872-1970): British philosopher and mathematician known for his work in logic, set theory, and philosophy of language.
- Jean-Paul Sartre(1905-1980): French philosopher and playwright known for his existentialist philosophy, which emphasizes the importance of individual freedom and responsibility.
- Noam Chomsky(1928-present): American philosopher and linguist known for his theory of universal grammar, which posits that all human languages share a common underlying structure.
Define Philosophies: Match Each Philosophy To The Correct Philosopher.
Philosophies are systems of thought that attempt to explain the fundamental nature of reality, human existence, and knowledge. They encompass a wide range of topics, including metaphysics, epistemology, ethics, and aesthetics.
Key Tenets of Major Philosophies
- Idealism: The belief that reality is fundamentally mental or spiritual in nature, and that the physical world is merely a manifestation of the mind.
- Materialism: The belief that reality is fundamentally physical in nature, and that the mind is a product of the brain.
- Rationalism: The belief that knowledge is derived primarily from reason and logic, rather than from experience or intuition.
- Empiricism: The belief that knowledge is derived primarily from experience and observation, rather than from reason or intuition.
- Existentialism: The belief that human beings are free and responsible for their own actions, and that the meaning of life is created by each individual.
- Utilitarianism: The belief that the right action is the one that produces the greatest happiness for the greatest number of people.
- Kantianism: The belief that morality is based on universal moral laws that are derived from reason, rather than from experience or intuition.
- Marxism: The belief that history is driven by economic forces, and that capitalism is an exploitative system that will eventually be replaced by a more just and equitable society.
- Pragmatism: The belief that the truth of a belief is determined by its practical consequences, rather than by its logical consistency or empirical verification.
- Postmodernism: The belief that there is no objective reality or truth, and that all knowledge is socially constructed.
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of matching philosophers to their philosophies?
Understanding the connections between philosophers and their philosophies provides a deeper comprehension of the historical context, influences, and evolution of philosophical thought.
How can we determine the correct match between a philosopher and their philosophy?
Matching philosophers to their philosophies involves examining their writings, teachings, and the historical record to identify the key tenets and ideas that align with each philosopher’s unique perspective.