Label the transmission electron micrograph of the mitochondria – Delving into the intricate realm of cellular biology, we embark on a journey to decipher the enigmatic transmission electron micrograph of mitochondria. This microscopic masterpiece unveils the hidden structures and functions that orchestrate the very essence of life.
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, hold a captivating complexity that has intrigued scientists for centuries. Their unique architecture, adorned with a symphony of membranes and compartments, conceals a symphony of biochemical reactions that sustain our existence.
Label the Structures: Label The Transmission Electron Micrograph Of The Mitochondria
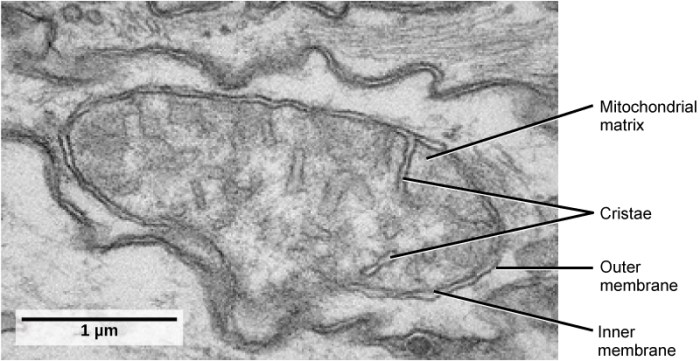
The transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of the mitochondria shows several distinct structures. These structures play vital roles in the functioning of the mitochondria, which is the powerhouse of the cell.
Identify the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane
The outer mitochondrial membrane is the outermost layer of the mitochondria. It is a phospholipid bilayer that contains proteins that regulate the passage of molecules into and out of the mitochondria.
Locate the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the innermost layer of the mitochondria. It is also a phospholipid bilayer, but it is folded into cristae. Cristae are shelf-like structures that increase the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, which is where ATP synthesis takes place.
Mark the Cristae
Cristae are shelf-like structures that increase the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane. They are the site of ATP synthesis, which is the process by which the mitochondria generate energy.
Point out the Mitochondrial Matrix
The mitochondrial matrix is the space enclosed by the inner mitochondrial membrane. It contains the enzymes involved in cellular respiration, which is the process by which the mitochondria generate energy.
Indicate the Location of Ribosomes, Label the transmission electron micrograph of the mitochondria
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are found on the outer mitochondrial membrane and on the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Describe the Function of Each Structure
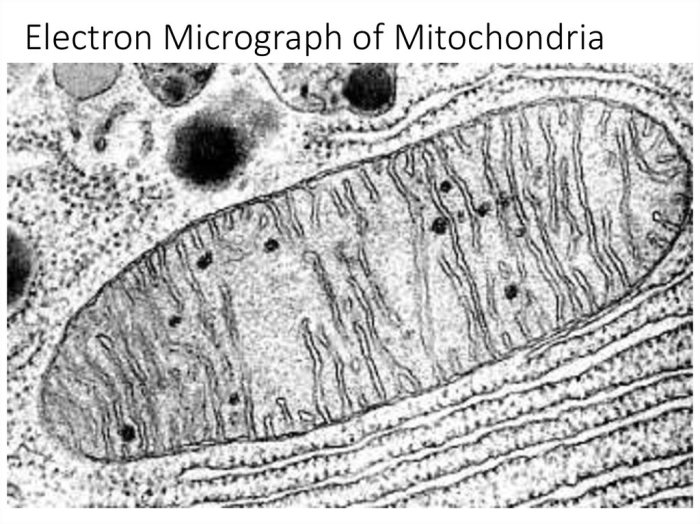
The structures of the mitochondria each play a vital role in the functioning of the cell.
Explain the Role of the Outer Mitochondrial Membrane in Regulating the Passage of Molecules
The outer mitochondrial membrane is responsible for regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the mitochondria. It contains proteins that allow certain molecules to pass through while blocking others.
Discuss the Function of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane in Energy Production
The inner mitochondrial membrane is responsible for energy production. It contains proteins that are involved in the electron transport chain, which is the process by which the mitochondria generate ATP.
Describe the Role of Cristae in Increasing the Surface Area for ATP Synthesis
Cristae are shelf-like structures that increase the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane. This increased surface area provides more space for the proteins involved in the electron transport chain, which allows the mitochondria to generate more ATP.
Explain the Function of the Mitochondrial Matrix in Housing the Enzymes Involved in Cellular Respiration
The mitochondrial matrix contains the enzymes involved in cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which the mitochondria generate energy. The enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix break down glucose and other nutrients to produce ATP.
Discuss the Role of Ribosomes in Protein Synthesis
Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis. They are found on the outer mitochondrial membrane and on the inner mitochondrial membrane. The ribosomes on the outer mitochondrial membrane synthesize proteins that are used in the mitochondria. The ribosomes on the inner mitochondrial membrane synthesize proteins that are used in the cytoplasm.
Compare the Structure of Mitochondria to Other Organelles
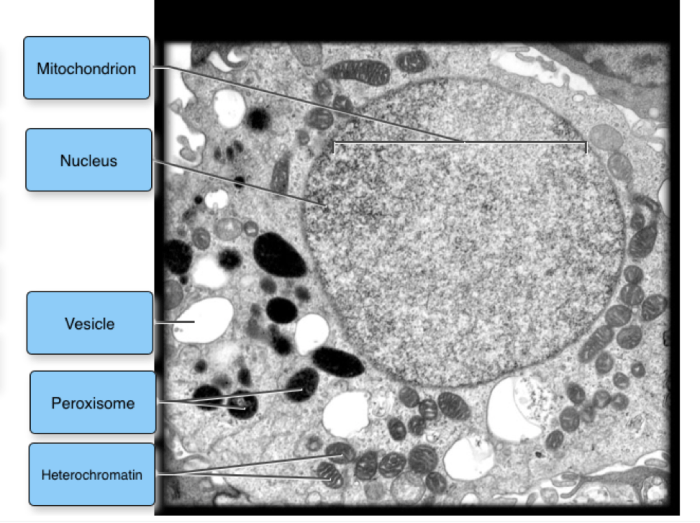
Mitochondria are similar in structure to other organelles in the cell. However, they have some unique features that distinguish them from other organelles.
Compare the Structure of Mitochondria to Chloroplasts
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are both organelles that are responsible for energy production. However, they have different structures. Mitochondria are found in all eukaryotic cells, while chloroplasts are only found in plant cells. Mitochondria are typically much smaller than chloroplasts. Mitochondria have a double membrane, while chloroplasts have a triple membrane.
Mitochondria contain cristae, while chloroplasts contain thylakoids.
Compare the Structure of Mitochondria to the Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are both organelles that are involved in protein synthesis. However, they have different structures. Mitochondria are typically much larger than the ER. Mitochondria have a double membrane, while the ER has a single membrane.
Mitochondria contain cristae, while the ER does not.
Compare the Structure of Mitochondria to the Nucleus
Mitochondria and the nucleus are both organelles that are responsible for genetic information. However, they have different structures. Mitochondria are typically much smaller than the nucleus. Mitochondria have a double membrane, while the nucleus has a single membrane. Mitochondria contain cristae, while the nucleus does not.
Explain the Importance of Mitochondria in Cellular Function
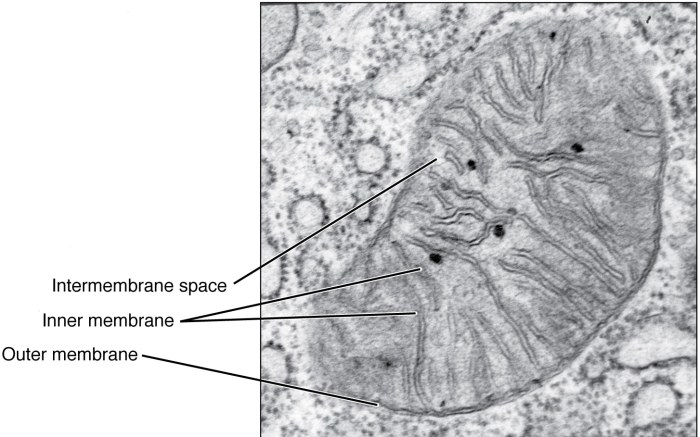
Mitochondria are essential for the proper functioning of the cell. They are responsible for generating energy, which is used to power all of the cell’s activities. Mitochondria are also involved in cellular respiration, which is the process by which the cell breaks down glucose and other nutrients to produce ATP.
Discuss the Role of Mitochondria in Energy Production
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell. They are responsible for generating ATP, which is the energy currency of the cell. ATP is used to power all of the cell’s activities, such as protein synthesis, cell division, and muscle contraction.
Explain the Role of Mitochondria in Cellular Respiration
Mitochondria are involved in cellular respiration, which is the process by which the cell breaks down glucose and other nutrients to produce ATP. Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. The enzymes in the mitochondrial matrix break down glucose and other nutrients to produce ATP.
Describe the Role of Mitochondria in Apoptosis
Mitochondria are involved in apoptosis, which is the process of programmed cell death. Apoptosis is a normal process that occurs in the body to remove damaged or unwanted cells. Mitochondria release proteins that trigger apoptosis when the cell is damaged or stressed.
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the outer mitochondrial membrane?
The outer mitochondrial membrane acts as a selectively permeable barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the mitochondrion.
What is the role of cristae in mitochondria?
Cristae are folded structures that increase the surface area of the inner mitochondrial membrane, providing ample space for ATP synthesis.
How do mitochondria compare to chloroplasts?
Both mitochondria and chloroplasts are organelles with double membranes, but mitochondria are involved in energy production while chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis.